Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health, especially for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. Blood sugar, or glucose, is the primary source of energy for the body’s cells. However, when blood sugar levels are too high or too low, it can lead to serious health complications. This article delves into the importance of blood sugar health and how glucose monitoring devices play a pivotal role in managing it.
Blood sugar levels are influenced by various factors, including diet, physical activity, stress, and medication. For individuals with diabetes, the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin (Type 1 diabetes) or doesn’t use insulin effectively (Type 2 diabetes). Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose enter the cells to be used for energy. Without proper insulin function, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to hyperglycemia (high blood sugar). Conversely, hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) can occur if there’s too much insulin or insufficient glucose intake.
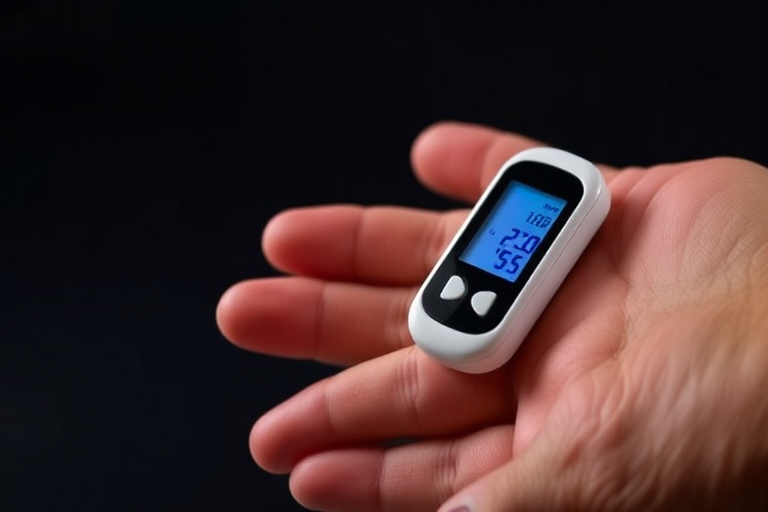
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential for managing diabetes and preventing complications. This is where glucose monitoring devices come into play. These devices provide real-time data on blood sugar levels, allowing individuals to make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and medication. There are several types of glucose monitoring devices available, each with its own set of features and benefits.
One of the most common types of glucose monitoring devices is the blood glucose meter. This portable device requires a small blood sample, usually obtained by pricking the finger with a lancet. The blood is then placed on a test strip, which is inserted into the meter. Within seconds, the meter displays the blood sugar level. Blood glucose meters are widely used due to their accuracy, affordability, and ease of use.
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) are another popular option. Unlike traditional blood glucose meters, CGMs provide continuous readings throughout the day and night. A small sensor is inserted under the skin, typically on the abdomen or arm, and measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid. The sensor sends data to a receiver or smartphone app, allowing users to track their blood sugar trends over time. CGMs are particularly beneficial for individuals who need to monitor their blood sugar levels closely, such as those with Type 1 diabetes or those experiencing frequent blood sugar fluctuations.
Flash glucose monitoring systems are a newer innovation in glucose monitoring technology. These systems use a sensor worn on the skin that measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid. Users can obtain glucose readings by scanning the sensor with a reader or smartphone. Flash glucose monitors offer the convenience of continuous monitoring without the need for finger pricks, making them an attractive option for many individuals.
In addition to these devices, there are also non-invasive glucose monitoring technologies in development. These technologies aim to measure blood sugar levels without the need for blood samples or skin penetration. Examples include optical sensors that use light to measure glucose levels and wearable devices that monitor glucose through sweat or tears. While these technologies are still in the experimental stages, they hold promise for the future of glucose monitoring.
Choosing the right glucose monitoring device depends on various factors, including the individual’s specific needs, lifestyle, and budget. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable option. Regardless of the device chosen, regular monitoring and proper management of blood sugar levels are key to maintaining good health and preventing complications.
In conclusion, blood sugar health is a critical aspect of overall well-being, particularly for individuals with diabetes. Glucose monitoring devices play a vital role in managing blood sugar levels, providing valuable data that can inform lifestyle and medical decisions. With advancements in technology, there are now more options than ever for monitoring blood sugar, making it easier for individuals to take control of their health.
